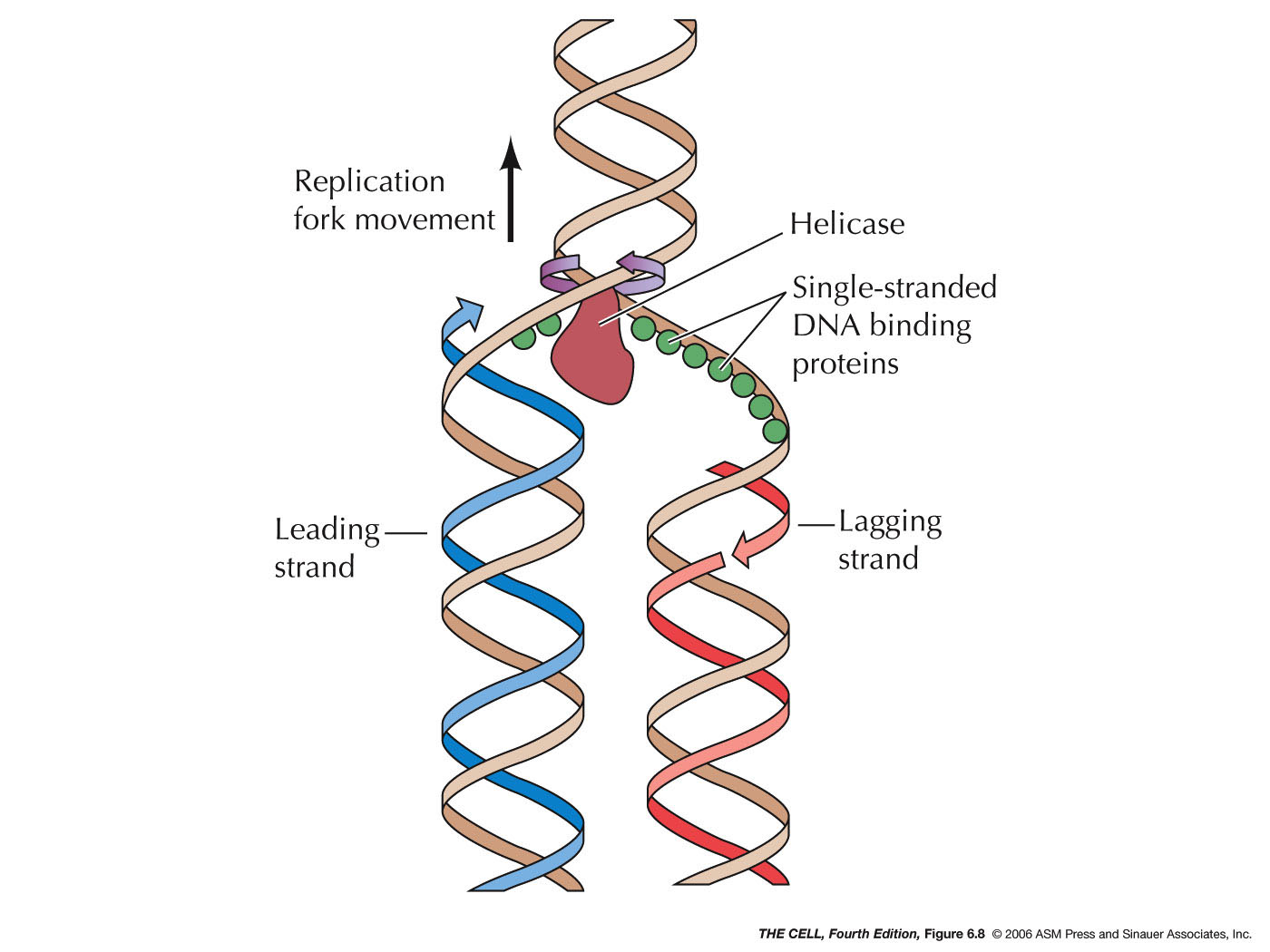
42 dna replication model with labels
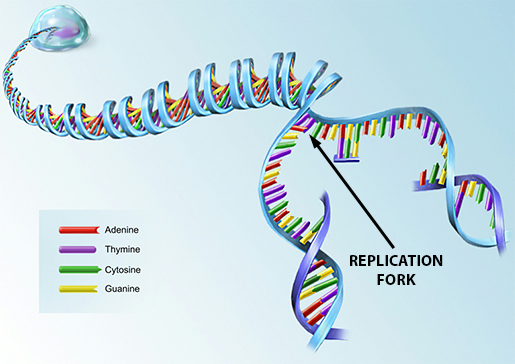
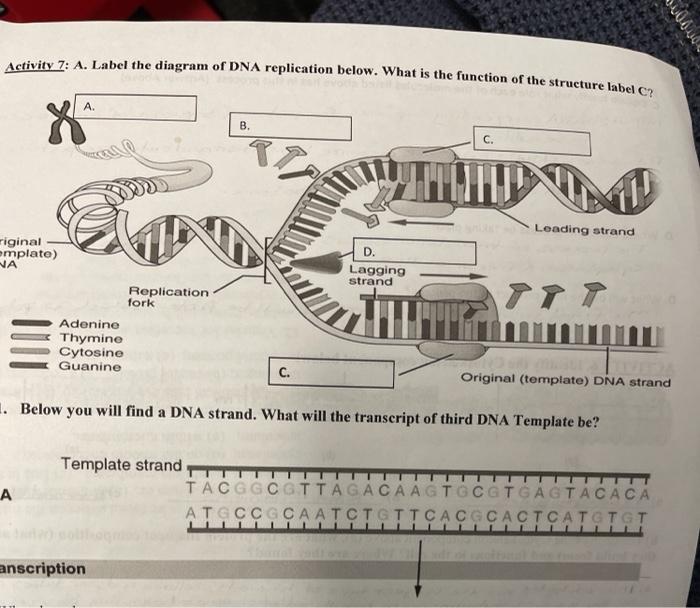
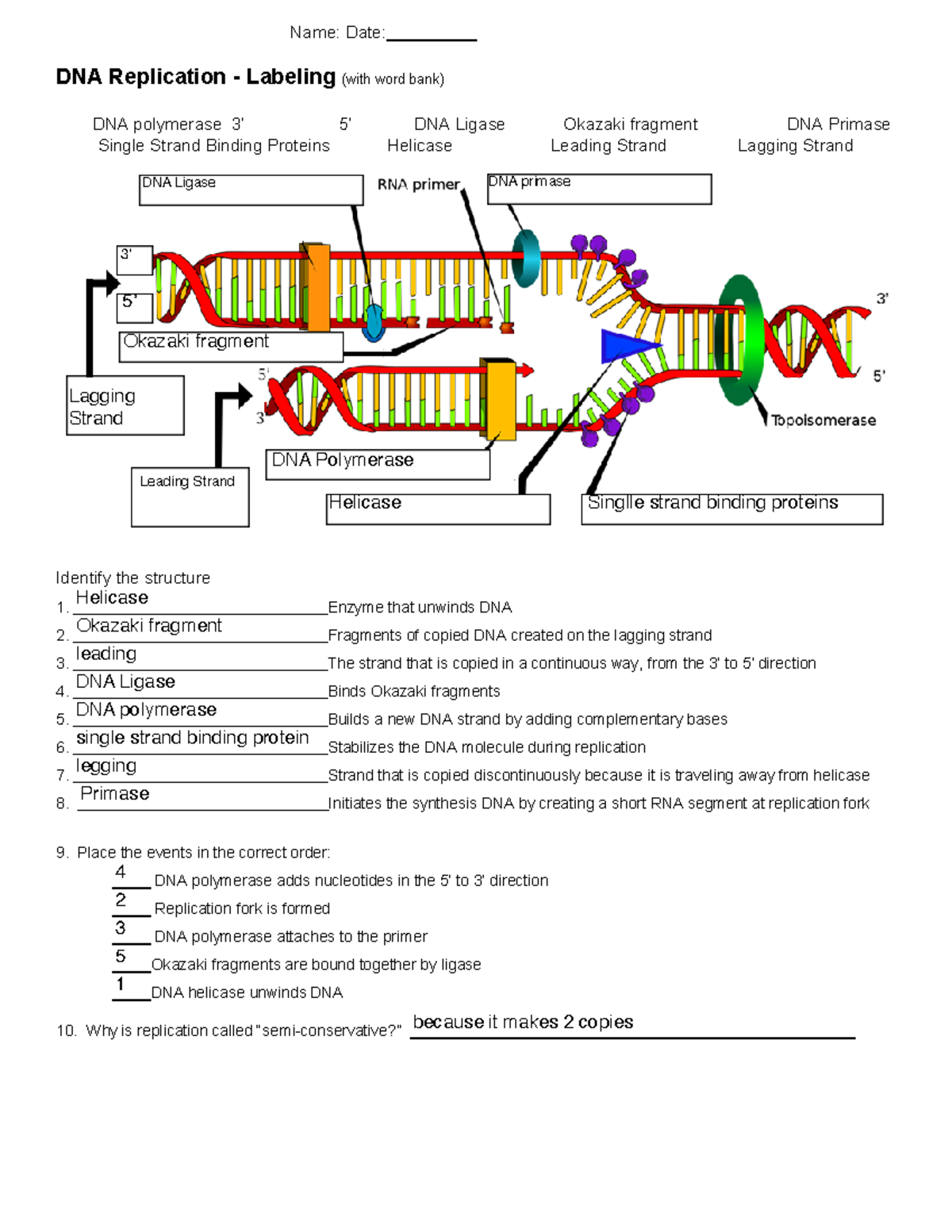
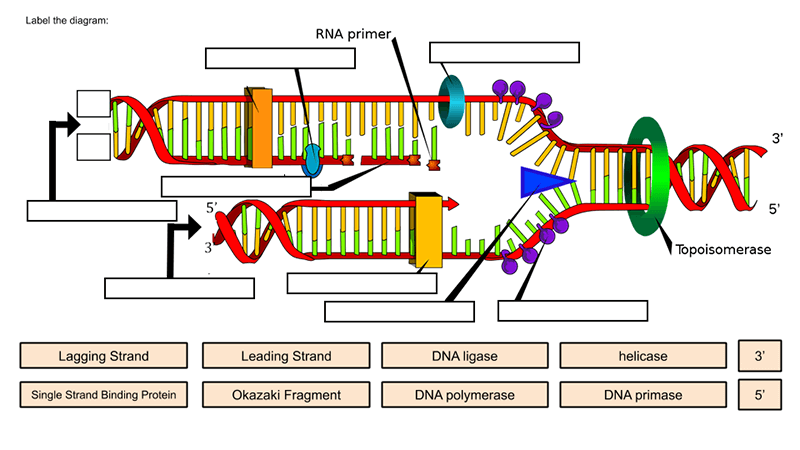
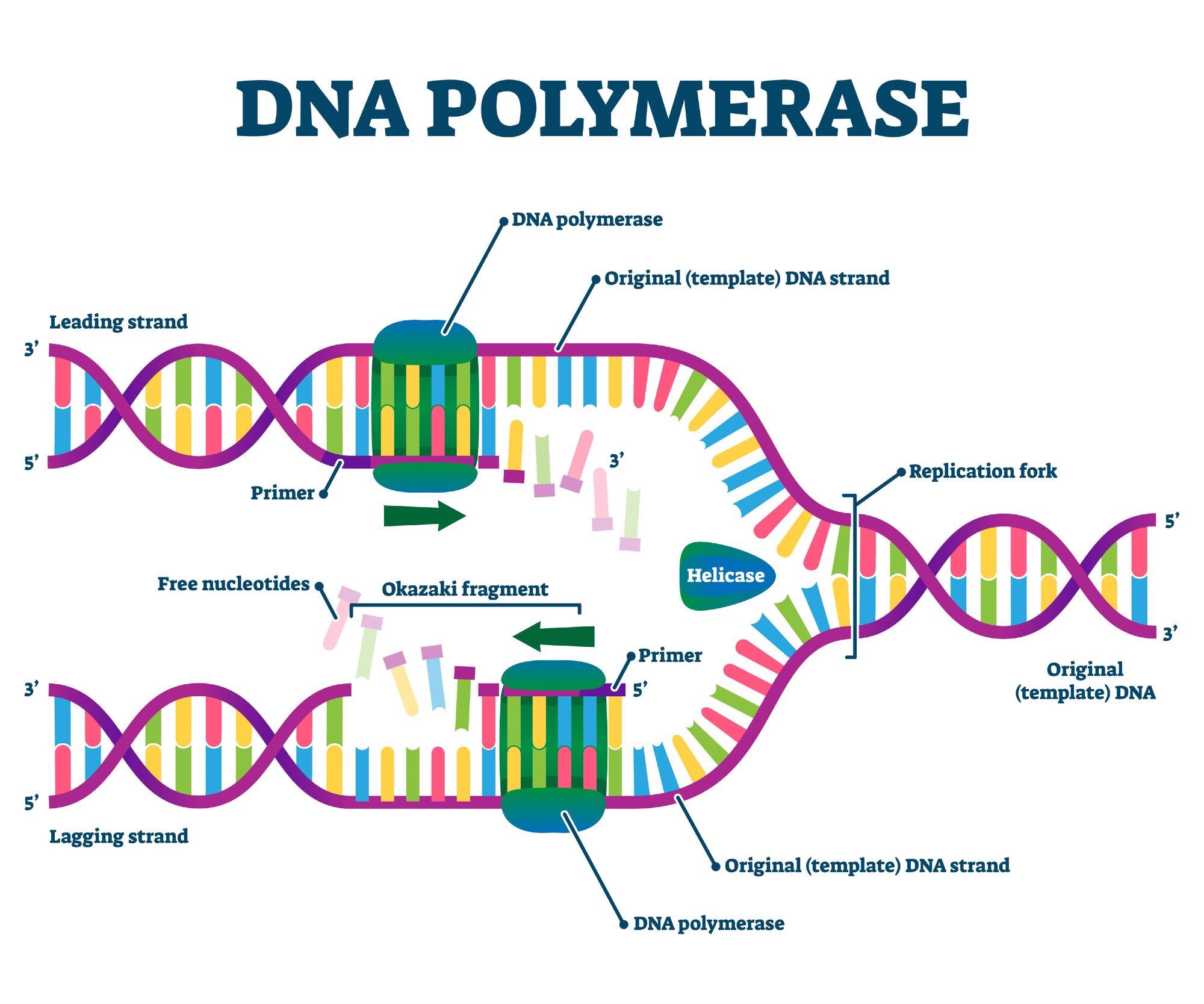
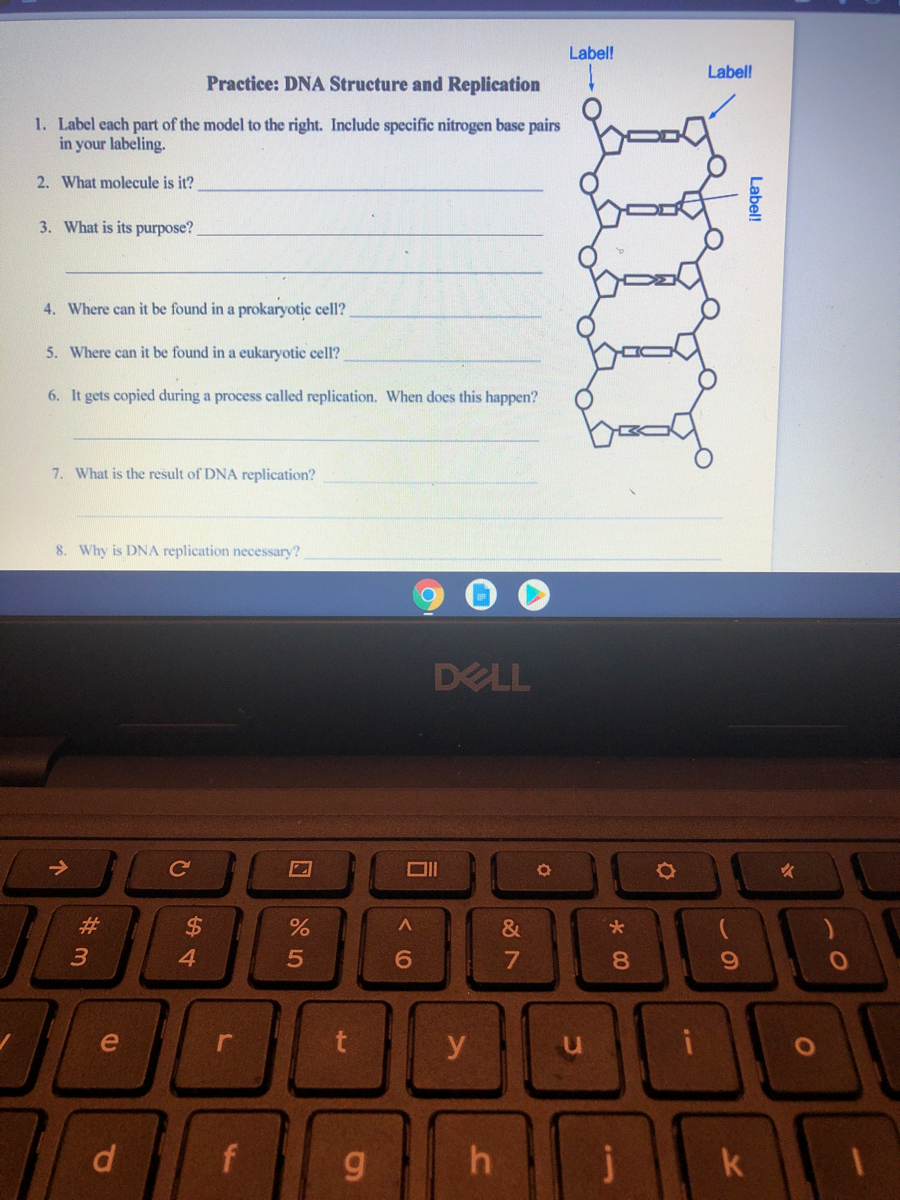
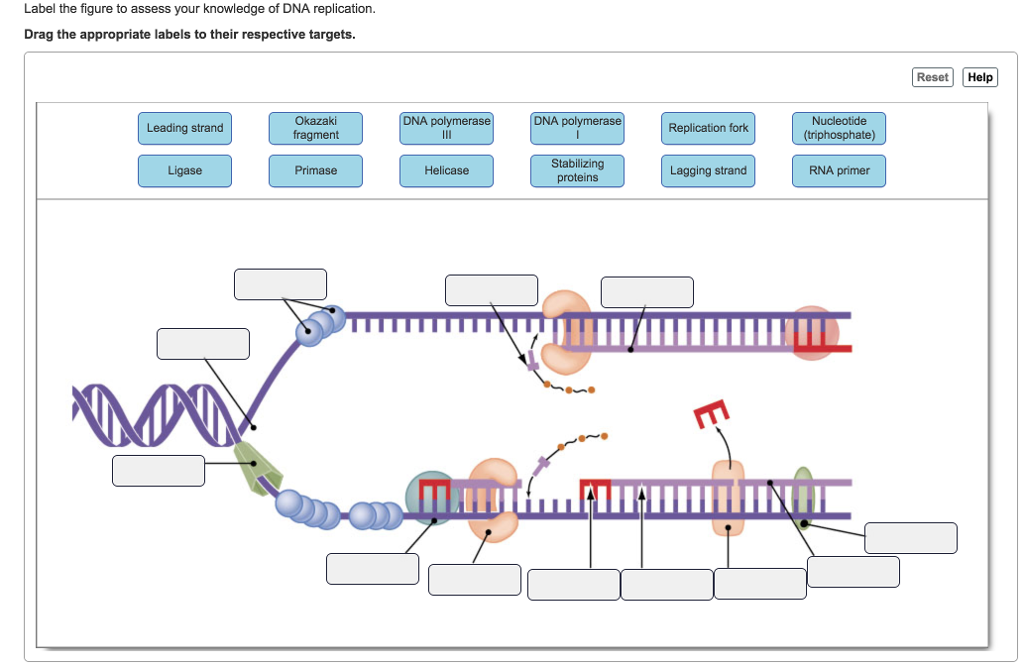
Label DNA and Replication - Google Slides Enzyme that unwinds DNA 2. Sections of copied DNA created on the lagging strand 3. The strand that is copied in a continuous way 4. Binds Okazaki fragments 5. Builds a new DNA strand by adding complementary bases 6. Stabilizes the DNA molecule during replication 7. Strand that is copied discontinuously 8. Initiates the synthesis DNA by creating ... DNA REPLICATION - Answers.pdf - DNA REPLICATION - ANSWERS a. Label the ... Label the following items: leading and lagging strands, Okazaki fragment, DNA polymerase, DNA ligase, helicase (the unwinding protein), single-strand binding proteins, RNA primer, replication fork, and 3' and 5' ends of all 4 DNA strands. b. Draw an arrow to indicate the overall direction of replication. Towards the replication fork.
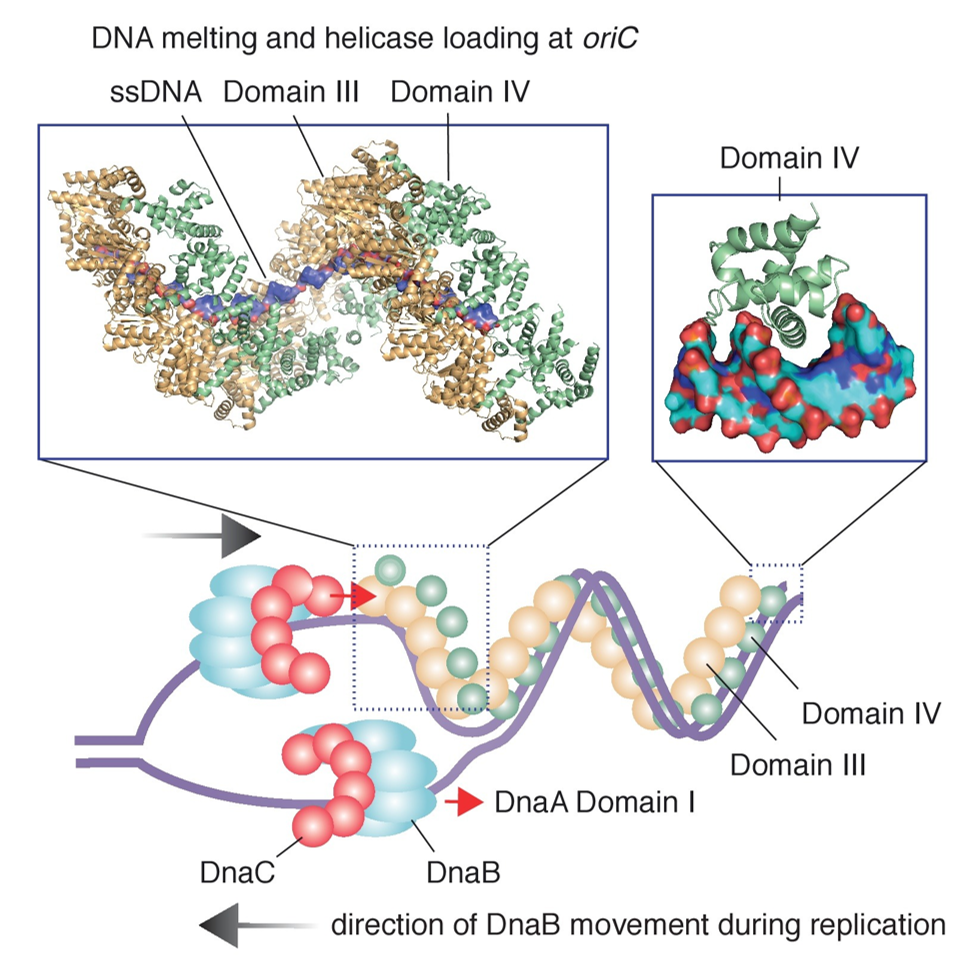
DNA Replication- Definition, enzymes, steps, mechanism, diagram DNA replication process uses DNA polymerase as the main enzyme for catalyzing the joining of deoxyribonucleoside 5′-triphosphates (dNTPs) forming a growing chain of DNA. Other proteins are also involved for initiation of the process and copying of DNA, along with proofreading capabilities to ensure the replication process takes place accurately.

Dna replication model with labels
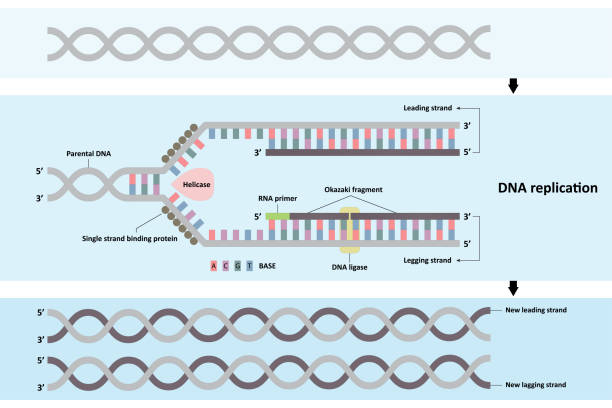
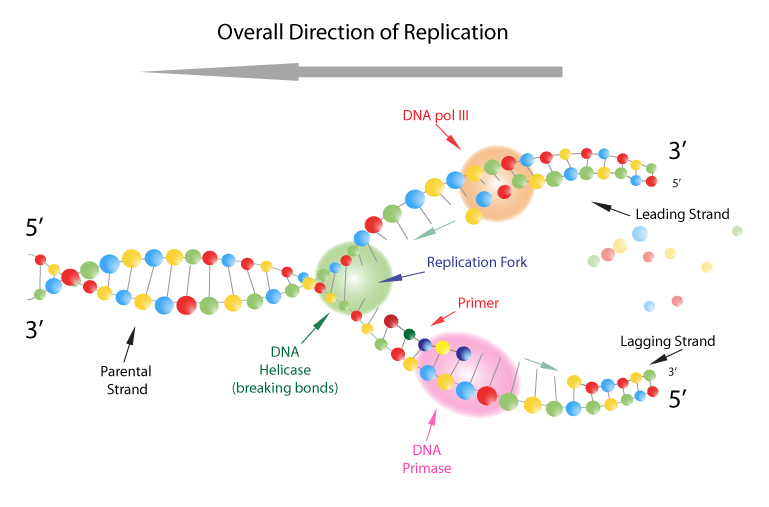
DNA Replication Labeling Diagram | Quizlet Primase An enzyme that creates a short RNA primer for initiation of DNA replication. RNA Primer short segment of RNA used to initiate synthesis of a new strand of DNA during replication The primer synthesized by primase enzyme DNA Polymerase on Leading Strand synthesizes new DNA only in the 5' to 3' direction Ligase DNA Replication: Definition, Mechanism, Significance - Embibe Mechanism of DNA Replication: DNA Replication Process. DNA Replication is a very unique and complex multistep biological process of producing two identical replicas from one original DNA molecule. It occurs in all living organisms (both prokaryotes and eukaryotes) because it forms an essential part of biological inheritance. DNA Replication Process with Diagrams Class 12 - Prokaryotic ... - BYJUS DNA Replication In the process of DNA replication, the DNA makes multiple copies of itself. It is a biological polymerisation, which proceeds in the sequence of initiation, elongation, and termination. It is an enzyme-catalysed reaction. DNA Polymerase is the main enzyme in the replication process. DNA Replication Process DNA Replication Steps
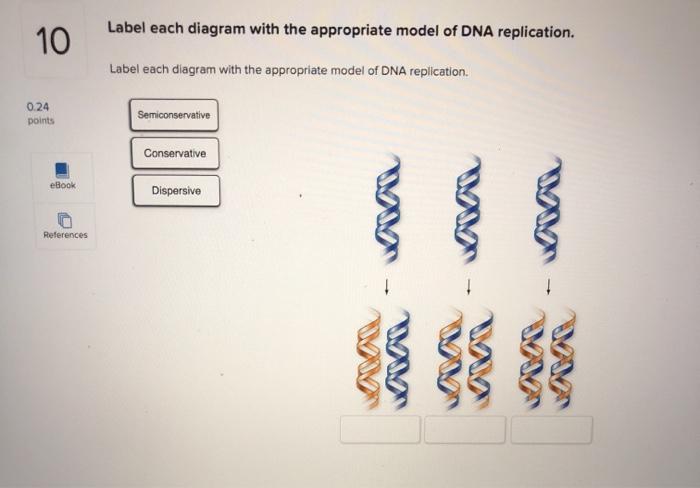
Dna replication model with labels. General Brigham | Integrated Health Care System Our physician-scientists—in the lab, in the clinic, and at the bedside—work to understand the effects of debilitating diseases and our patients’ needs to help guide our studies and improve patient care. DNA Replication (With Diagram) | Molecular Biology DNA Replication is Semi-Conservative: Watson and Crick model suggested that DNA replication is semi-conservative. It implies that half of the DNA is conserved. Only one new strand is synthesized, the other strand is the original DNA strand (template) that is retained. Each parental DNA strand serves as a template for one new complementary strand. DNA replication: Explanation, Process & Steps | StudySmarter DNA replication occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle, illustrated below.This happens within the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The DNA replication that occurs in all living cells is termed as semiconservative, meaning that the new DNA molecule will have one original strand (also called the parental strand) and one new strand of DNA. This model of DNA replication is most widely accepted ... Semiconservative Replication of DNA - Mechanism Dispersive replication: In this model, DNA replication makes two molecules that are a mix of parent and daughter DNA. These molecules are called "hybrids." In this model, each strand is made up of pieces of old and new DNA. At the time, most biologists probably would have bet on the semi-conservative model.
Mastering Quiz: Chapter 7A Microbial Genetics Flashcards | Quizlet a. mRNA is transcribed from DNA in the cytoplasm. b. mRNA binds directly to amino acids during translation. c. mRNA includes a cap that consists of extra adenine nucleotides. d. Segments of mRNA that code for protein are removed before translation. e. mRNA moves from the nucleus to the cytoplasm following RNA processing. DNA Replication Process with Diagrams Class 12 - Prokaryotic ... - BYJUS DNA Replication In the process of DNA replication, the DNA makes multiple copies of itself. It is a biological polymerisation, which proceeds in the sequence of initiation, elongation, and termination. It is an enzyme-catalysed reaction. DNA Polymerase is the main enzyme in the replication process. DNA Replication Process DNA Replication Steps DNA Replication: Definition, Mechanism, Significance - Embibe Mechanism of DNA Replication: DNA Replication Process. DNA Replication is a very unique and complex multistep biological process of producing two identical replicas from one original DNA molecule. It occurs in all living organisms (both prokaryotes and eukaryotes) because it forms an essential part of biological inheritance. DNA Replication Labeling Diagram | Quizlet Primase An enzyme that creates a short RNA primer for initiation of DNA replication. RNA Primer short segment of RNA used to initiate synthesis of a new strand of DNA during replication The primer synthesized by primase enzyme DNA Polymerase on Leading Strand synthesizes new DNA only in the 5' to 3' direction Ligase























Post a Comment for "42 dna replication model with labels"